Galloping and Setting Up for Cross-Country Fences: A Conversation with Captain Mark Phillips

Cross-country riding is basically galloping across the country, jumping various obstacles. The ability to transition from the gallop to the appropriate speed and balance for the upcoming obstacle is an essential skill for riding cross-country. It is a skill that needs to be practiced just as jumping the actual fences needs to be practiced. Recently I had a conversation with Captain Mark Phillips about how to do this.
THE CONVERSATION
Back when I was competing at the 5* level and being coached by Capt. Mark Phillips, I asked him for help because I was having trouble getting my horse back for the straight forward galloping fences at the Advanced speed. I didn’t want to just let my horse gallop to the fences unchecked, but I also didn’t want to do too much because that cost time and sometimes interfered with the rhythm resulting in a chip in or an awkward distance to a big fence. The discussion that followed helped me understand what I needed to do, and I recently had a chance to review the topic with Capt. Mark.
First, I should say that Capt. Mark didn’t like the term “getting my horse back” because of the backward connotations. So I will be using the term “setting up” in this article as it suggests preparation and upward balance, which is what we want.
In answer to my question, Capt. Mark went on to explain “setting up” to me in this way. He asked how fast my horse would be galloping between fences. The optimum speed at the Advanced level is 570 meters/minute. Since I would need to slow down for the technical fences and combinations, I would need to go faster than 570 meters/minute between fences to make up time, so my speed between fences might be 600 meters/minute.
Next Capt. Mark asked what I thought my horse’s stride length would be at a galloping speed of 600 meters/minute. I guessed maybe 18 feet. (The specifics don’t matter here.) He said, ok, then if I were to maintain the same rhythm, what would my horse’s stride length be if I were to slow down to 500 meters/minute? I thought that if I were to maintain my rhythm but slow my speed, that would require a shorter stride length, so my stride length might be 15 feet. He said good, then to set up correctly, I should:
- Change the horse's speed (but not the speed of his feet) by shortening his stride length through a more upward balance.
- Change the horse’s balance by bringing my seat closer to the saddle and bringing my shoulders up.
ILLUSTRATING THE CONCEPT
The diagrams below illustrate this concept of changing the horse’s speed while maintaining the same rhythm and impulsion. In the diagrams, each bump represents one gallop stride, and the horizontal axis represents the distance covered in one minute. (The values used for rhythm and speed were chosen to simplify the diagrams and do not represent actual rhythms and speeds found in cross-country riding.)
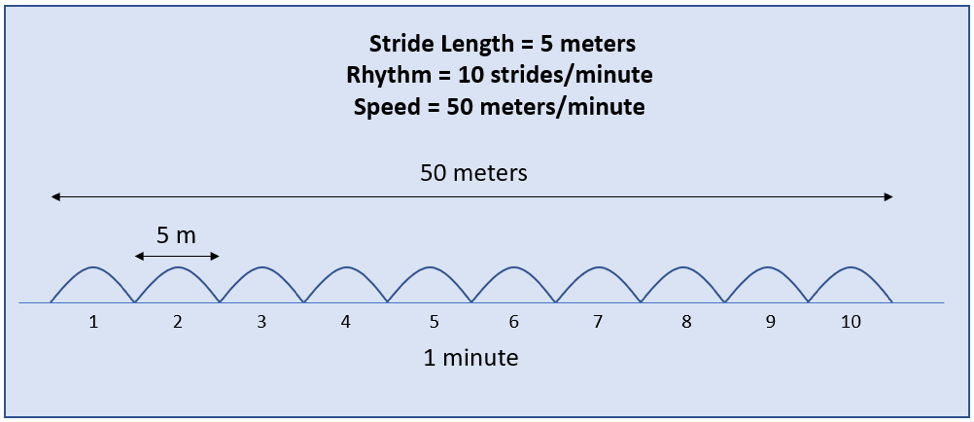
The first diagram illustrates a 5-meter stride length at a rhythm of 10 strides/minute. This rhythm and stride length would produce a speed of 50 meters/minute.
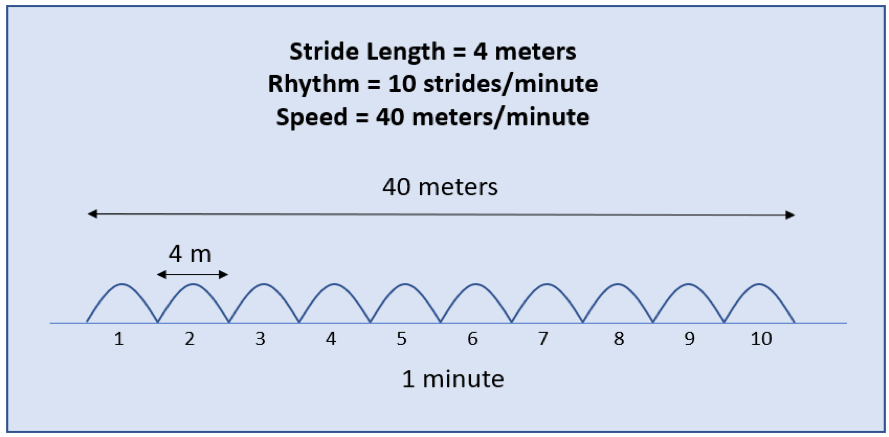
The second diagram illustrates a 4-meter stride length at the same rhythm of 10 strides/minute. Since the stride length has changed, the distance covered in 1 minute has been reduced to 40 meters/minute, which is exactly what we wanted to accomplish: reducing the speed while maintaining the rhythm and the impulsion. Only the stride length has changed.
HOW TO PRACTICE AND TRAIN YOUR HORSE
This critical skill of shortening the horse’s stride length and bringing their balance up while maintaining the speed of their feet and impulsion is easier said than done. Like anything else involved with riding well, it requires practice and training. So practice. Train your horse to understand what you’re asking for. You don’t even need jumps or a cross-country course to work on this skill. A big arena or field where you can gallop a little will do the trick.
To practice, start with a nice forward canter or slow gallop. Then shorten your horse’s stride by changing its balance. Do this by supporting the horse with your leg, bringing your shoulders up, and taking a soft feel upward and forward of the mouth. Don’t pull with your hand or slow their feet. Use as much leg as you need to keep their feet active and their front end up. Balance is always supported by the rider’s leg (inside calf muscle).
When practicing on hotter horses, they may not want to slow their gallop given only these subtle aids. If you use your hand too strongly, they will most likely tighten in the neck and back and pull against you. If this happens, you may want to try the following exercise:
- From a forward canter, ask the horse to move from one leg into the opposite hand. To do this, support the horse with your outside leg and outside hand, nudge them with your inside leg, and squeeze your fingers on the inside rein to encourage the horse to move over and remain supple in their neck (just like in the dressage arena!). Do not pull back on the reins to balance up and shorten the stride. This will cause the horse to pull against you.
Introducing this hint of lateral suppleness should help soften the horse over the topline and allow them to shorten their stride. Start by asking for just a little shortening. If the horse gives you what you want, reward them by letting them go forward for a few strides. Go forward with them, loosening your elbows and following their mouth with your hand. Then ask again for shortening, asking for more as they come to understand what you want.
When practicing on quieter horses, touching the reins with too much hand may cause them to slow their feet and lose impulsion, so be sure to use your leg before your hand. If the feet slow down, immediately apply the leg (and the crop if necessary) to keep their feet active. The impulsion that you will need to jump the fences comes from active feet.
If you are competing at the higher levels and your horse hasn’t learned this “setting up” skill yet, you may need to begin setting up quite far in advance of vertical fences or technical combinations to be sure that you have the correct speed and balance for the question at hand. This will take more time, but it will hopefully save you from an unfortunate run-out or an awkward jump from a bad distance.
EXAMPLES OF SETTING UP
If you want to see great examples of this “setting up” skill, check out videos of Phillip Dutton, Boyd Martin, William Fox-Pitt, Piggy French, or Harry Meade going around a cross-country course. These experts are so good at galloping and jumping that you can’t even see them setting up for the fences. Their hands barely move, and their horse’s gallop remains active and rhythmic. But don’t be fooled. . . they’re doing exactly the right amount of work. It’s just not visible because these horses are well trained to understand what their riders are asking for.
Incidentally, this lengthening and shortening of the frame and the stride isn’t anything new to our event horses. This action is asked for in most dressage tests. The only difference is that you are asked to shorten and lengthen at the walk, trot, and canter in dressage. In cross-country, you are asked to do it at a gallop.
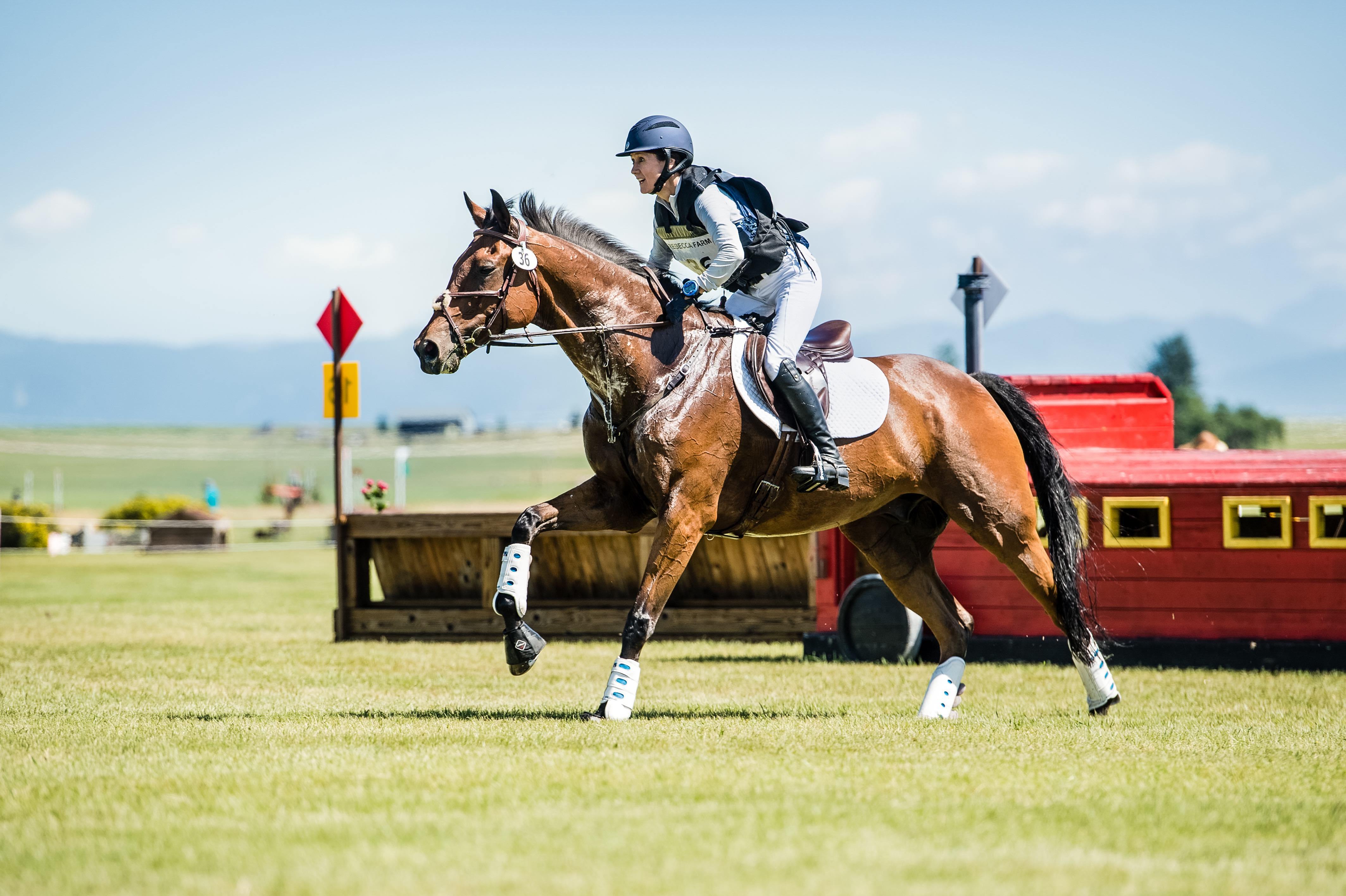

The photo above shows the horse and rider galloping. The horse’s head and neck are lowered and stretched out. The rider is up out of the saddle, going forward with the horse. Here the stride will be longer, and the speed will be faster.
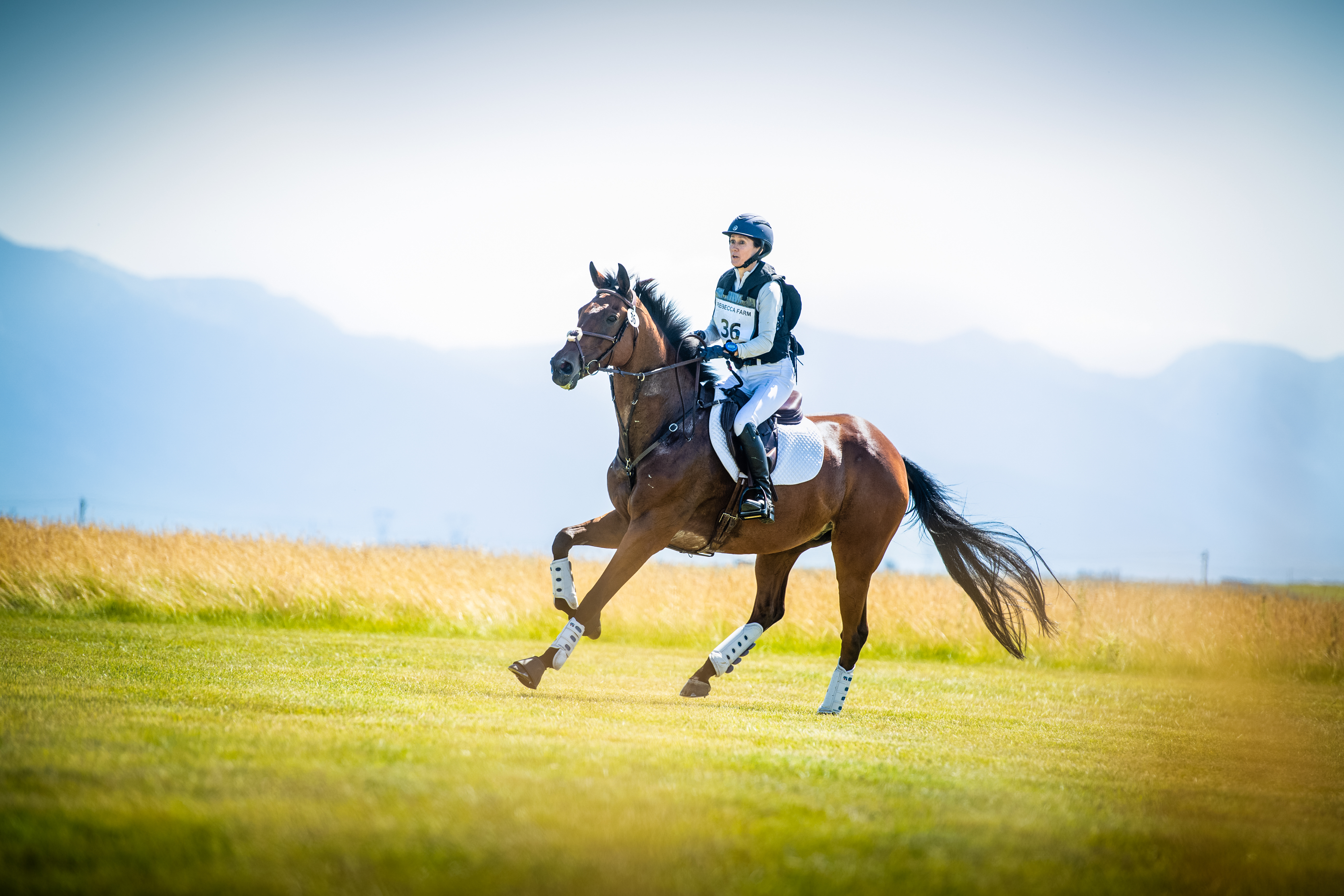

The photo above shows the horse and rider setting up for a fence. The rider has closed their leg against the horse’s side, lowered their seat toward the saddle, lifted their shoulders, and taken a light feel of the mouth. In response, you can see that the horse has shifted its weight more to the hind legs, lifted its head and neck, and both horse and rider appear to be focused on the upcoming obstacle.
HOW MUCH TO SET UP
At the lower levels of competition, where the speeds are lower, and the fences are more straightforward, less setting up is needed. But riding cross-country at these levels provides a great opportunity to teach the horse rhythm, straightness, and lightness in front of the fences. You can work on these things:
- Try to maintain the same rhythm (speed of the feet) around the whole course.
- If your horse starts to back off of an upcoming obstacle, keep your leg on. Don’t let them lose impulsion or slow the speed of their feet. And be sure to keep them straight.
- If your horse starts to run off or speed up, settle them back into your original rhythm by supporting with your leg and balancing them up by gently taking and letting go with the reins. Don’t brace your hand against their mouth.
- Introduce some lightness of the forehand on the approach to the fences. This can be as simple as the horse pricking up its ears and raising its head and neck to look at the upcoming jump. Or it may be you raising your shoulders a few inches to signal to the horse that it should balance up within its canter rhythm.
More setting up will be required at the upper levels because the galloping speeds are higher, and the fences are larger and more technical. How much to set up will depend on the speed of the gallop, the profile of the fence, and the question being asked by the upcoming obstacle or combination.
- Rampy galloping fences will require less setting up. Eventually, you hope to be able to set up for these fences by simply bringing your seat closer to the saddle and raising your shoulders to balance up.
- Vertical fences and technical combinations will require a more significant shortening of stride length (speed reduction) and a greater upward balance.
- If there is a bend or turn on the approach to your fence, less setting up will be needed from you since turning requires you to sit up, touch the reins, and guide the horse with your leg.
CONCLUSION
I want to thank Captain Mark Phillips for taking the time to share some of his vast knowledge of cross-country riding and for helping put his marvelous explanations and advice down on paper.
To summarize, Capt. Mark said this:
“The most difficult part of cross-country riding is to persuade yourself to use your leg before your hand. The second most difficult part is to balance up and forward, and not to pull back to adjust your speed.”

About Captain Mark Phillips
Captain Mark Phillips rode for the British Eventing Team for 20 years. During his career he won the 5-star event at Badminton four times, along with numerous gold and silver medals at the Olympics, World Championships, and European Championships. Capt. Phillips then took on the role of Chef d’Equipe of the U.S. Eventing Team. He led the team for 20 years, helping them to win 26 medals at the Olympics, World Championships, and Pam Am Games. Currently Capt. Phillips focuses on cross-country course design. He has designed courses across the United States and Europe, most notably the 5-star courses at Burghley and Luhmühlen, and the FEI World Equestrian Games™ Tryon 2018 course.















